QUORA SERIES | PART 3 | Tactics for E-commerce Fraud Prevention
If you are new to the “QUORA SERIES”, here’s what you need to know:
A few months ago, we asked the following question on Quora:
As an e-commerce business owner, what are your top 3 problem areas?
(Link to this Quora question is provided at the end of the blog)
One of the recurring concerns provided by respondents is e-commerce cybersecurity and fraud prevention.
Let’s look at the two answers that mentioned this:
The first answer has been written by Harsh Patel who is the founder of a news and media company that provides coverage on topics like retail & e-commerce, startups, finance, etc. Here’s what he has to say:
“Online Security and Fraud Prevention: Protecting customer data and maintaining online security is paramount. Implementing robust security measures, such as SSL encryption, secure payment gateways, and fraud detection systems, helps safeguard customer information and build trust.”
New York-based Henry P., an e-commerce web developer in a leading company, has also written about e-commerce cybersecurity in his answer:
“Cybersecurity: eCommerce businesses face the risk of cyber attacks that can compromise sensitive customer information such as credit card numbers and personal data. This can lead to loss of customer trust, financial loss and legal consequences.”
So here we are, addressing e-commerce cybersecurity in Part 3 of the Quora series.
Types of E-commerce Fraud
The problem with e-commerce is, the more it grows, the more e-commerce fraud grows. So before getting into e-commerce fraud prevention, let’s understand the common types of e-commerce cybersecurity attacks your business could be prone to.
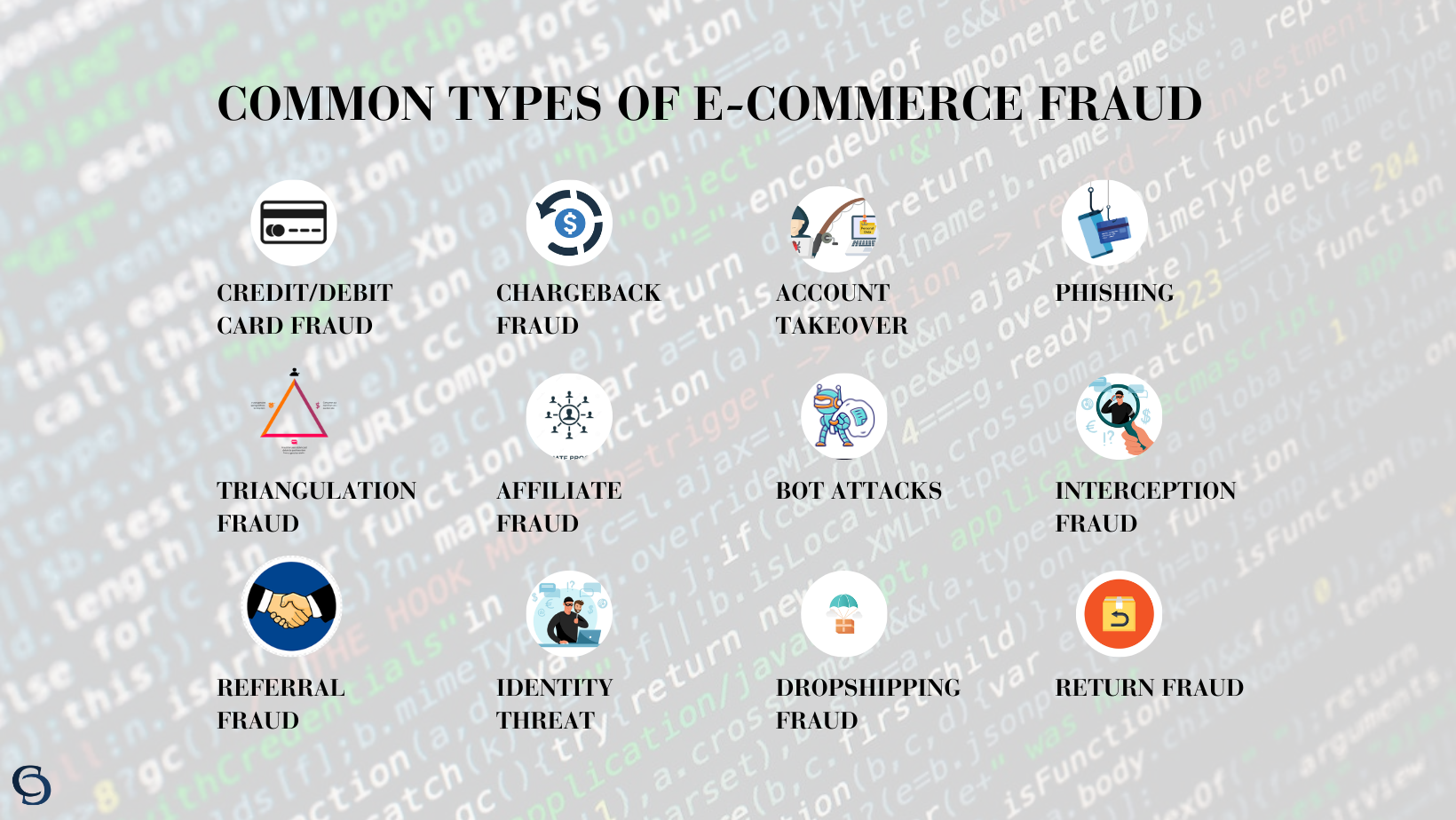
E-commerce Cybersecurity Fraud 1:Chargeback Scams
Sneaky customers may try to get a refund after making a purchase by claiming they didn’t get the goods or never made the purchase, leaving you in the lurch.
What it looks like:
A fraudster places an order for expensive electronics, such as a high-end smartphone, from your e-commerce store using a stolen credit card. After receiving the product, the fraudster contacts their bank and claims that they never received the item. The bank then issues a chargeback, and you lose both the product and the payment.
E-commerce Cybersecurity Fraud 2: Account Takeover
Imagine someone hacking into a customer’s account, and then they go on a shopping spree, pretending to be the customer.
What it looks like:
A hacker gains access to a customer’s account on your e-commerce platform by using stolen login credentials acquired from a previous data breach on another website. Once inside, the hacker can make purchases using the stored payment methods and then change the shipping address to divert goods for their own gain.
E-commerce Cybersecurity Fraud 3: Card Testing
Fraudsters test stolen credit card details by making small purchases to see if they work. If they do, they might go for the big haul!
What it looks like:
Fraudsters obtain a list of stolen credit card details from the dark web. To verify which cards are active and valid, they use automated bots to make small purchases from various e-commerce websites. If the test transaction goes unnoticed, they proceed to make larger unauthorized purchases.
E-commerce Cybersecurity Fraud 4: Phishing
Watch out for those fake emails or websites that trick customers into revealing sensitive info like credit card numbers.
What it looks like:
Scammers send out deceptive emails posing as your e-commerce store or a trusted payment processor. The email may contain a link to a fake website that looks identical to yours, asking customers to update their account details or payment information. Unsuspecting customers fall victim to the phishing scam and unknowingly share sensitive data with fraudsters.
E-commerce Cybersecurity Fraud 5: Affiliate Fraud
Affiliate fraud involves dishonest affiliates who use deceptive practices to earn illegitimate commissions from an e-commerce company’s affiliate marketing program.
What it looks like:
An affiliate marketer artificially inflates the number of clicks or leads generated through their affiliate links. They may use automated bots, incentivize fake sign-ups, or engage in cookie-stuffing techniques. As a result, you end up paying commissions for fake leads or clicks that didn’t result in genuine sales.
E-commerce Cybersecurity Fraud 6: Dropshipping Fraud
In this type of fraud, dishonest dropshippers exploit the dropshipping model to jeopardize e-commerce cybersecurity.
What it looks like:
A dropshipper partners with an e-commerce store and lists products for sale on their website. Customers place orders and pay for the items. However, the dropshipper never fulfills the orders, leaving the e-commerce store to deal with angry customers who paid for products that were never delivered. The dropshipper disappears, leaving the store to handle refunds and customer complaints.
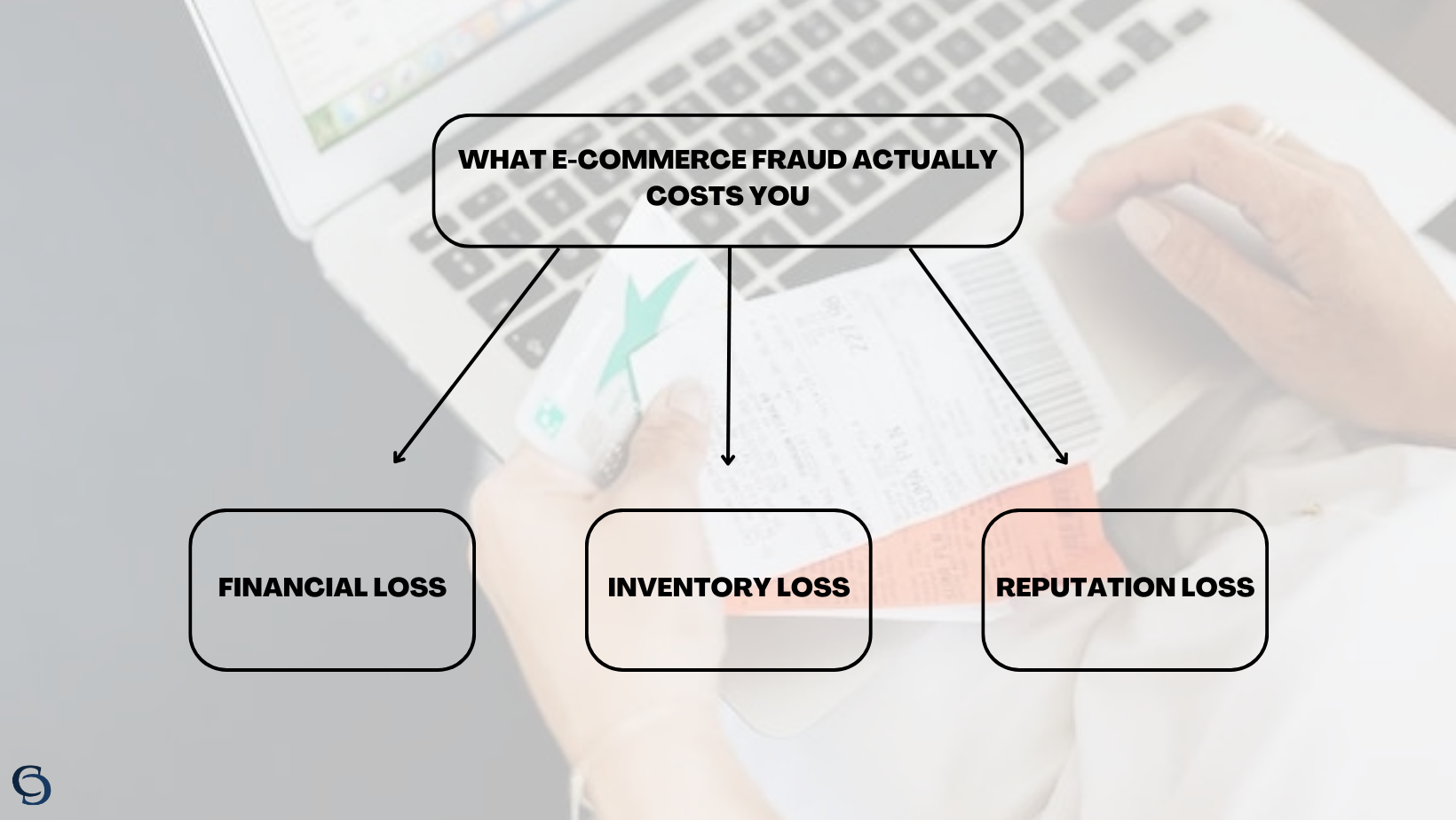
The Real Cost of E-commerce Fraud
Fraud isn’t just a minor annoyance; it’s a financial nightmare. One of the most immediate and tangible consequences of e-commerce fraud is the dreaded chargeback. Not only do these chargebacks mean you lose hard-earned revenue from fraudulent transactions, but you also bear the burden of additional chargeback fees. These mounting financial losses can put a severe strain on your bottom line, affecting your ability to invest in growth and expansion.
But it doesn’t stop there. Fraud doesn’t just snatch your revenue; it can rob you of your valuable inventory as well. Fraudsters often use stolen credit card information to place orders, and once the real cardholders detect the fraudulent transactions, they demand refunds. Your precious inventory goes out the door, only to be snatched back, leaving you with empty shelves and frustrated customers.
Yet, the damage doesn’t end with financial losses; your brand’s reputation is also at stake. In the digital age, word travels at the speed of light, and a single instance of fraud can ripple through the internet like wildfire. Customers who fall victim to fraud on your platform will not only abandon your store but are likely to share their negative experiences with others, tarnishing your hard-earned reputation.
To survive and thrive in the cutthroat e-commerce landscape, fraud prevention must become a non-negotiable priority. Investing in robust e-commerce fraud prevention measures isn’t just a smart business decision; it’s a survival strategy. By proactively safeguarding your business and customers from fraud through e-commerce cybersecurity measures, you can protect your hard-earned revenue, preserve your valuable inventory, and safeguard the reputation you’ve worked so tirelessly to establish.
Ways to Prevent E-commerce Cybersecurity Fraud
E-commerce Cybersecurity Tactic 1: Implement HTTPS
- Get an SSL certificate from a trusted CA
- Install it on your web server and update URLs to “https://”
- Enable HTTP to HTTPS redirects
- Test for mixed content issues and fix them
- Update Google Search Console and XML sitemap
- Update robots.txt and social media links
With HTTPS, you secure your e-commerce site, protect customer data, and build trust. Customers are more likely to transact when they see “https://” and the padlock icon, ensuring a safer shopping experience.
E-commerce Cybersecurity Tactic 2: Ensure PCI Compliance for Your Store
To make your business PCI compliant, it’s crucial to follow the guidelines set forth by the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Start by thoroughly understanding the specific requirements of PCI DSS and assessing your current security measures to identify any potential vulnerabilities. Implement strong security controls, such as firewalls, encryption, access controls, and regular system updates, to address these weaknesses and align with PCI standards. Utilize secure payment gateways that comply with PCI requirements to safeguard sensitive payment data during transactions.
Regular monitoring and testing are essential to maintain compliance and proactively prevent fraud. Conduct vulnerability scans and penetration testing at regular intervals to identify and resolve potential risks promptly. Prioritize employee training on security best practices and implement awareness programs to foster a security-conscious culture within your organization. Collaborate with PCI-compliant third-party vendors and consider a formal PCI audit by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) for additional validation of your compliance efforts.
E-commerce Cybersecurity Tactic 3: Use Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification before granting access to their accounts or completing sensitive transactions. Here’s where to implement MFA on your e-commerce site:
Account Login:
Require MFA during the login process to ensure that only authorized users can access their accounts. When users attempt to log in, prompt them to enter a one-time verification code sent to their registered email or mobile device. This extra step ensures that even if a password is compromised, the account remains protected.
High-Risk Transactions:
Enforce MFA for high-risk transactions, such as large purchases, address changes, or account updates.
Customer Registration:
During the account registration process, offer users the option to enable MFA. Encourage them to set up MFA by explaining its security benefits and the peace of mind it provides.
Admin and Employee Access:
If your e-commerce site has an administrative panel or employee access, MFA should be mandatory. Protecting sensitive data and critical operations from unauthorized access is essential for overall security.
Implementing MFA can be achieved through various methods:
- SMS/TEXT & EMAIL VERIFICATION: Send a one-time code to the user’s registered mobile number or email address and they enter it during login or transaction verification.
- AUTHENTICATOR APPS: Encourage users to use authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or Authy. These apps generate time-based codes, providing an additional layer of security.
Remember to communicate the importance of MFA to your customers and assure them that it’s a proactive measure to safeguard their accounts and sensitive information.
E-commerce Cybersecurity Tactic 4: IP address and geolocation
Leveraging IP address and geolocation data is a smart approach to bolstering your e-commerce site’s fraud prevention strategy. Here’s how to do it:
Order Verification:
During the checkout process, cross-reference the user’s provided shipping address with their IP address location. If there’s a significant mismatch (e.g., the IP address is from a different country than the shipping address), consider flagging the transaction for manual review or requesting additional verification from the user.
Anomaly Detection:
Monitor for irregular patterns in IP addresses. For instance, if a single user’s account is suddenly accessed from multiple geographically distant locations within a short period, it might indicate unauthorized access. Implement alerts or temporarily block such activities until the user verifies their identity.
Geolocation Restrictions:
If you predominantly serve customers within a specific region, consider restricting transactions originating from high-risk countries or regions notorious for fraudulent activities. This can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized transactions.
Device Fingerprinting:
Combine IP and geolocation data with other parameters like device type, browser, and user behavior to create a unique “fingerprint” for each user. This allows you to track and recognize returning users and quickly identify any anomalies.
User Authentication:
Use IP and geolocation data to enhance user authentication. If a user logs in from an unrecognized IP address or location, prompt them for additional verification steps, such as a one-time code sent to their email or mobile.
To implement IP address and geolocation effectively, integrate third-party APIs or tools that provide accurate IP address and geolocation data. These services offer real-time insights to inform your fraud prevention decisions. Work with your development team to set up custom rules based on IP and geolocation data. Tailor these rules to your specific business model and customer demographics.
E-commerce Cybersecurity Tactic 5: Conduct Velocity Checks
Velocity checks involve monitoring the frequency and volume of transactions from a single source, be it an IP address, a device, or an account.
Transaction Frequency:
Set predefined limits on the number of transactions that can be initiated from a single source within a specific timeframe. If the limit is exceeded, flag the transactions for manual review or implement an automatic block.
Order Value:
Keep an eye on the total value of transactions coming from a single source. Unusually high or rapid purchases could indicate fraudulent behavior. Implement thresholds that trigger alerts or additional verification steps for such transactions.
Account Creation:
Monitor the speed at which new accounts are being created from the same IP address or device. A sudden surge in account registrations might signal fraudulent intent. Implement a cooling-off period before a new account can make substantial transactions.
Geographical Analysis:
Combine velocity checks with IP address and geolocation data. If multiple transactions are originating from different locations in a short span, it could be a red flag.
User Behavior:
Assess whether the transaction patterns align with the user’s historical behavior. Sudden deviations, like a large number of high-value transactions in a short period, should trigger further scrutiny.
Things You Can Start Doing Now to Preserve E-commerce Cybersecurity
Immediate Action Plan 1: Conduct Site Security Audit
Start by asking these questions:
- Are all shopping cart software and plugins updated to the latest versions?
- Are security patches applied promptly?
- Is your SSL certificate current and functioning correctly?
- Is data transmission between your store and users encrypted?
- Is your online store compliant with PCI-DSS standards for secure payment handling?
- Are you backing up your online store regularly to prevent data loss?
- Are strong, unique passwords used for admin accounts, hosting dashboards, CMS, databases, and FTP access?
- Are regular scans conducted to detect and remove malware from your website?
- Is communication between your store, customers, and suppliers encrypted for data security?
- Have inactive or unnecessary plugins been removed to reduce vulnerabilities?
Immediate Action Plan 2: Monitor Transactions and User Behavior
Common fraudulent behavior to track include:
- Multiple failed login attempts
- Sudden surge in orders
- Rapidly changing IP address
- Numerous purchase attempts using different credit cards
- Orders shipped to different addresses with similar details
- Purchases that don’t align with users’ historical behavior, such as suddenly buying high-value items
- Rapidly adding and removing items from the cart
- Frequent changes in the device used for transactions, especially during checkout
Immediate Action Plan 3: Eliminate Non-Physical Address Entries
Fraudsters often exploit anonymity by employing PO boxes or obscure addresses, evading detection. To counter this, refrain from shipping orders to PO boxes and virtual addresses linked to freight forwarders. Recognizable by container numbers in the address, these addresses should be flagged and excluded to enhance fraud prevention measures.
Immediate Action Plan 4: set Purchase Limits
Implement purchase limits to curb excessive transactions from a single source. This deters fraudsters from attempting to exploit your system for monetary gain.
Immediate Action Plan 5: reduce Sensitive Data collection
Reduce risk by collecting only essential customer data. Avoid storing sensitive information unless necessary, and use encryption to secure stored data, mitigating potential breaches. Sensitive data that you should avoid requesting (if necessary, avoid storing) include:
- Social Security Number
- CVV or PIN
- Bank account number
- Health information
- Full birth dates
Immediate Action Plan 6: Train Your Staff
Start by organizing comprehensive training sessions that cover various aspects of fraud prevention. Provide real-life examples and case studies to illustrate different fraudulent scenarios. Teach your staff how to spot unusual purchasing patterns, mismatched billing and shipping addresses, and suspiciously large orders. Highlight the importance of verifying customer identities when dealing with high-value transactions or unfamiliar customers. Establish a protocol for reporting potential fraud or suspicious behavior promptly. Regularly update your team on emerging fraud trends and tactics to keep their knowledge current.
Consider implementing role-specific training to address the unique challenges each team member might face. For instance, your customer service team should be well-versed in verifying customer identities.
Immediate Action Plan 7: Educate Your Customers
Provide guidelines on creating strong passwords, recognizing phishing attempts, and promptly reporting suspicious activities. If your website requires sensitive customer information, it’s important to be clear about how it will be used. Have encryption in place to protect the data and provide assurance that it will not be stored or shared with a third party, in addition to undertaking other privacy measures.
how codaemon can help with e-commerce cybersecurity
There is an array of sophisticated software tools like Cloudflare, Kount, Signifyd, etc. to fortify your digital storefront against cybercrime. These solutions are designed to provide a multi-layered defense, from the initial point of entry to the final transaction. We can help you identify the right set of tools for your business. We understand that the nuances of your operations demand a personalized approach to fraud prevention. Our team will conduct a thorough assessment of your e-commerce ecosystem, taking into account factors such as transaction volume, customer demographics, and the types of products or services you offer. Based on this, we will curate a tailored selection of software solutions that align precisely with your needs and help you integrate them.
Get in touch with us at (888) 811-3073 or send an email to support@codaemon.com.
Link to the Quora Question: As an e-commerce business owner, what are your top 3 problem areas?
Read Part 1 of the Series: QUORA SERIES | PART 1 | HOW TO CHOOSE THE BEST PRODUCT TO SELL ONLINE
Read Part 2 of the Series: QUORA SERIES | PART 2 | ATTRACT CUSTOMERS TO YOUR ONLINE STORE: LONG-TERM CUSTOMER ACQUISITION STRATEGIES
